What do the two most important stakeholder groups want from an insurance company?
An insurance policy serves to transfer the financial aspects of a risk from a person to an insurance company. It is based on a social principle: That this risk transfer costs the same for everyone when the same risks are selected. If they have to make a claim, customers expect a reliable, quick, and easy service. Investors buy shares in insurance companies because of the long-term, secure dividends. These companies have stable business models, and the returns they generate are very attractive.
The digital challenges for insurance companies
Customer behavior is changing. Young customers are less loyal. Fully digital and flexible products and services are essential. The same goes for omnichannel strategies for advisory services, sales, and other services. Insurance companies should interact more frequently with their customers — on easy-to-use digital channels.
The market is putting pressure on prices. New competitors and intermediaries are entering the market. What’s more, price transparency is becoming more detailed, which makes it easier for consumers to compare offers. Distribution costs are very high, and exclusive distributors and brokers have to significantly improve their productivity.
Product administration needs to be simpler, more flexible, and more digital
Insurance companies should take proactive steps to reduce claims inflation And they have to make sure that claims handling meets customers’ digital requirements.
Additionally, the insurance industry is suffering from the shortage of skilled workers.
The five investment priorities
Digital transformation is not an end in itself. Insurance companies need to develop digital capabilities that meet customer requirements. A sustainable and strategic approach is crucial here:
Augmented advisory services: Brokers and agencies need digital support for the sales process. The key here is making sure that they can focus on giving advice. Companies should aim to fully automate policy administration and issuing certificates. In addition, they should use Copilot AI and LLM solutions to support their advisors and answer questions about policy terms. Advisors should have a 360-degree view of their customers. After all, having additional information provides opportunities to give good advice — and opportunities for proactive sales.
Beyond insurance: In the future, insurance companies will be part of various ecosystems. They will be integrated into ecosystems for banking, pensions, home, SMEs, and health. This will provide opportunities to obtain more information about their customers and make sales. In these ecosystems, differentiated partner services such as prevention services will increase customer loyalty.
Zero ops: Insurance companies need to fully automate their operational processes. Manual interventions should be rare. When they are needed, AI should augment them. This means reading documents automatically, identifying requests, and handling them digitally. Digital interactions with customers should take place via a secure messaging board. In addition, insurance companies need to define and automate their oversight and compliance processes.
Digital products for digital natives: Insurers need to create simple, modular products that consumers can combine to suit their needs. Service levels should be clear, and services need to be accessible. Coverage checks and claims handling should be digitalized and mobile-friendly.
Open pensions: Financial transparency in old-age provision is becoming more important: Insurance companies need to identify pension gaps earlier. They should make proposals for ensuring quality of life in old age and communicate them clearly to customers via digital channels.
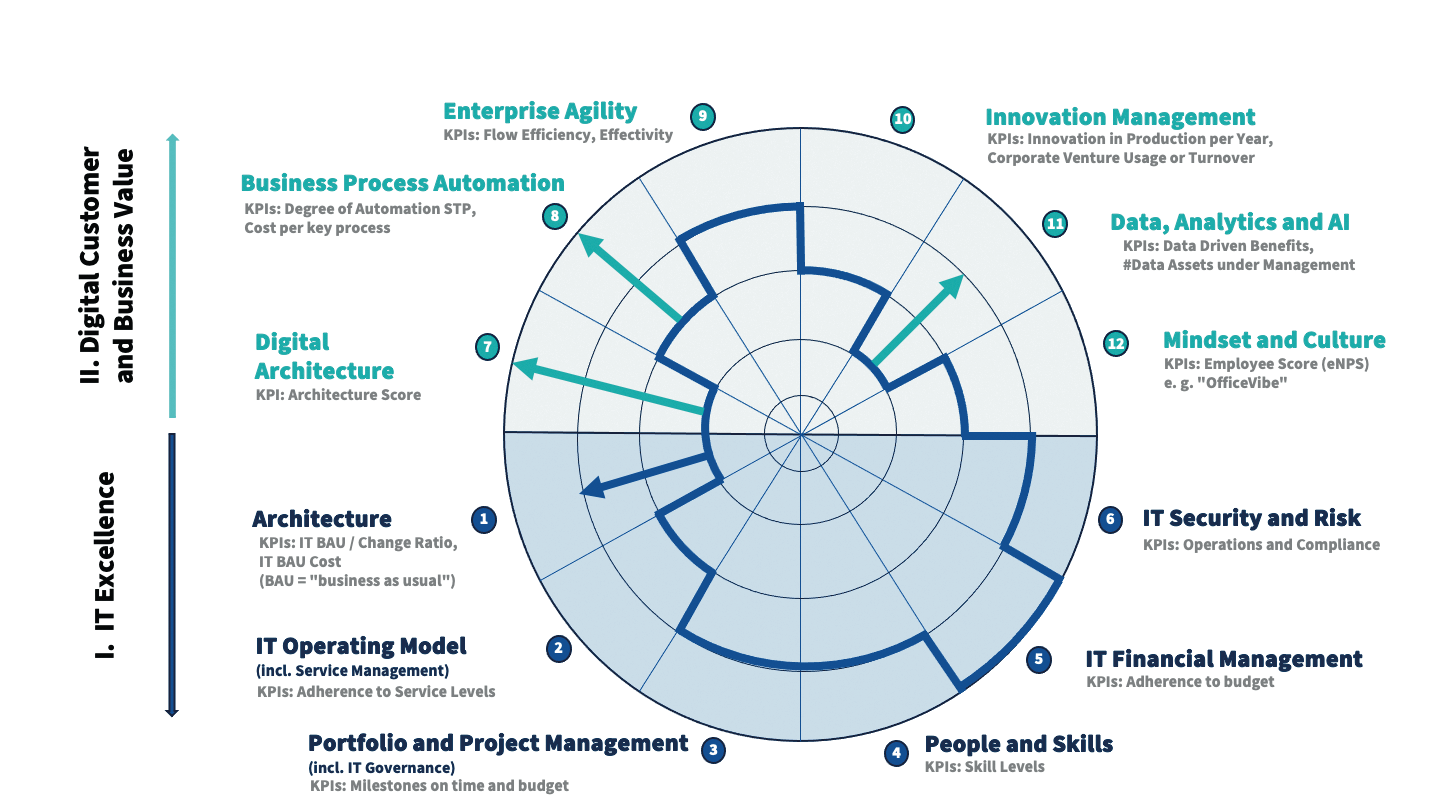
The twelve capabilities needed to achieve these ambitions
To achieve these five investment priorities, insurance companies need to define their required digital capabilities and determine their current level of maturity:
Finding the right partner
Insurance companies will not be able to do all this on their own. They will need expert partners who bring technology and business expertise to their projects. ti&m has the essential core competencies as a tech and data partner to support insurance companies inthe next steps of their digital transformation.
Integrating the entire value chain
What do insurance companies need to look for in a strategic, long-term partner? One of the two most important requirements is the ability to tick all the boxes: developing and evaluating various solutions through consulting, helping shape business requirements, and quickly developing an MVP. Working with mobile, UX, and design thinking methods, for example, that open up new perspectives. Integrating security considerations into the design right from the start. And using agile teams to develop products with the insurer and expand its core landscape.
Technological core competencies and on-premises specialists
These four dimensions are the biggest drivers for future value generation: Digital architecture: All insurers will invest in developing new cloud-native applications. In addition, they are migrating their core applications to the cloud and modernizing them. This means modularizing and virtualizing applications and automating testing. In the future, insurers will use software to configure their infrastructures and automate application integration and configuration management via scripting. Faster development cycles but also the need for resilience and reversibility will dictate the requirements for this.
Business process automation and augmentation: As described above, insurers will digitalize their current business models over the next ten years. They have to significantly improve the productivity of their consultants and in-house operations through business process automation (BPA). To achieve this, insurers need a taxonomy for process management, automation frameworks, metrics for performance management, and the technologies to implement them. Using AI analytics to evaluate process data will provide additional information.
Data, analytics, and AI: Data governance, data management, data architecture, master data and metadata management, quality management, data security and privacy management, data leakage and lineage, ethics and compliance — these are all essential for building analytical rules and models. Of course, modern technologies are also needed — and the three major cloud hyperscalers will supply them. On this basis, insurers will be able to develop and test value-enhancing models — and then apply them. The most important areas of application are in Customer 360, risk selection and pricing, claims leakage and fraud prevention, and document intelligence.
Security technologies: Using new technologies also means applying modern and robust security concepts.
Insurers are facing complex business and technology challenges. To tackle them, working with competent IT partners such as ti&m is crucial. Together, they need to analyze their strategic requirements and identify the necessary tech and data capabilities. Their ultimate goal must be to develop software solutions that meet the needs of their customers and employees.